Let's dive in:
Why T-Pot?
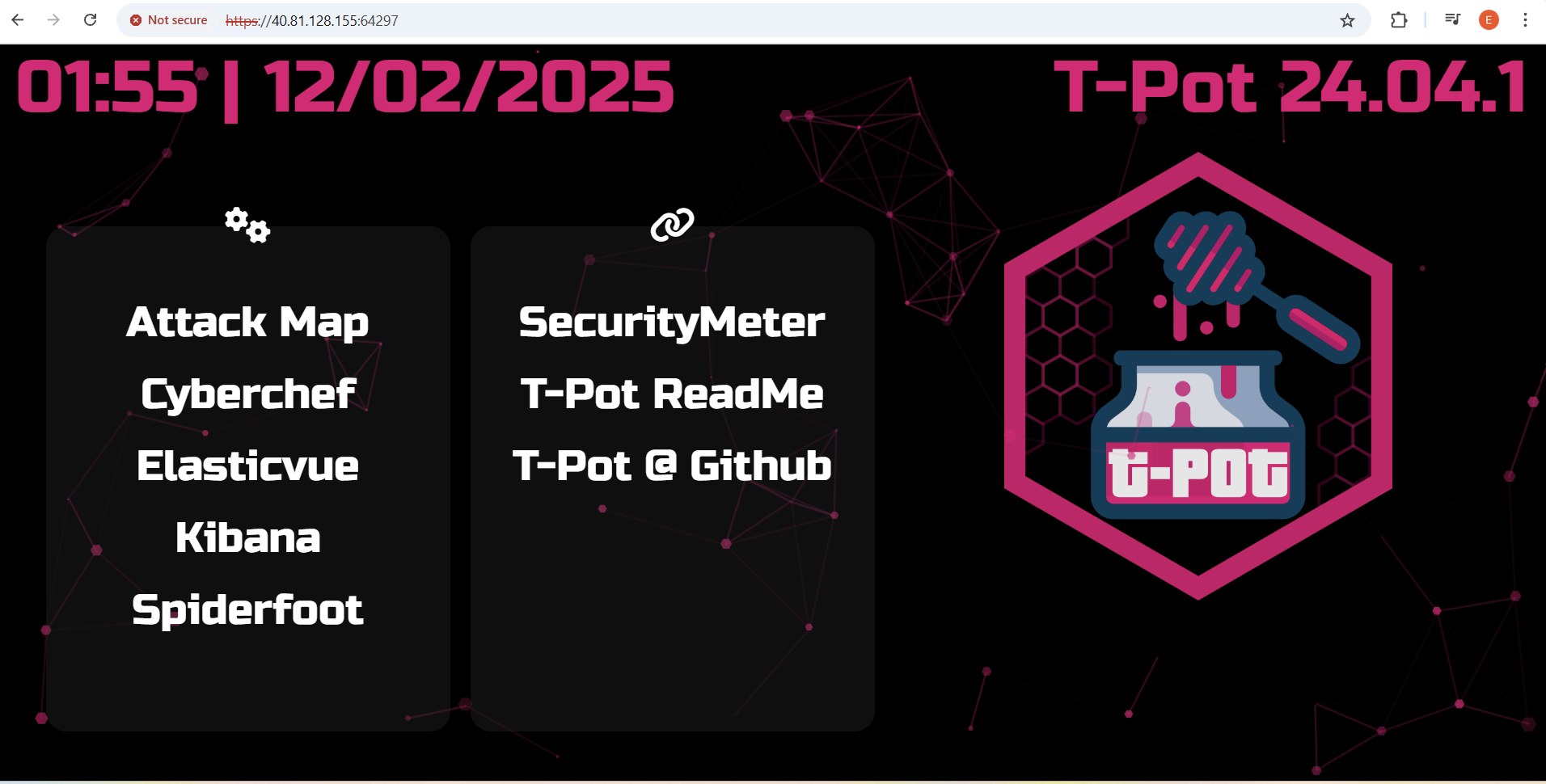
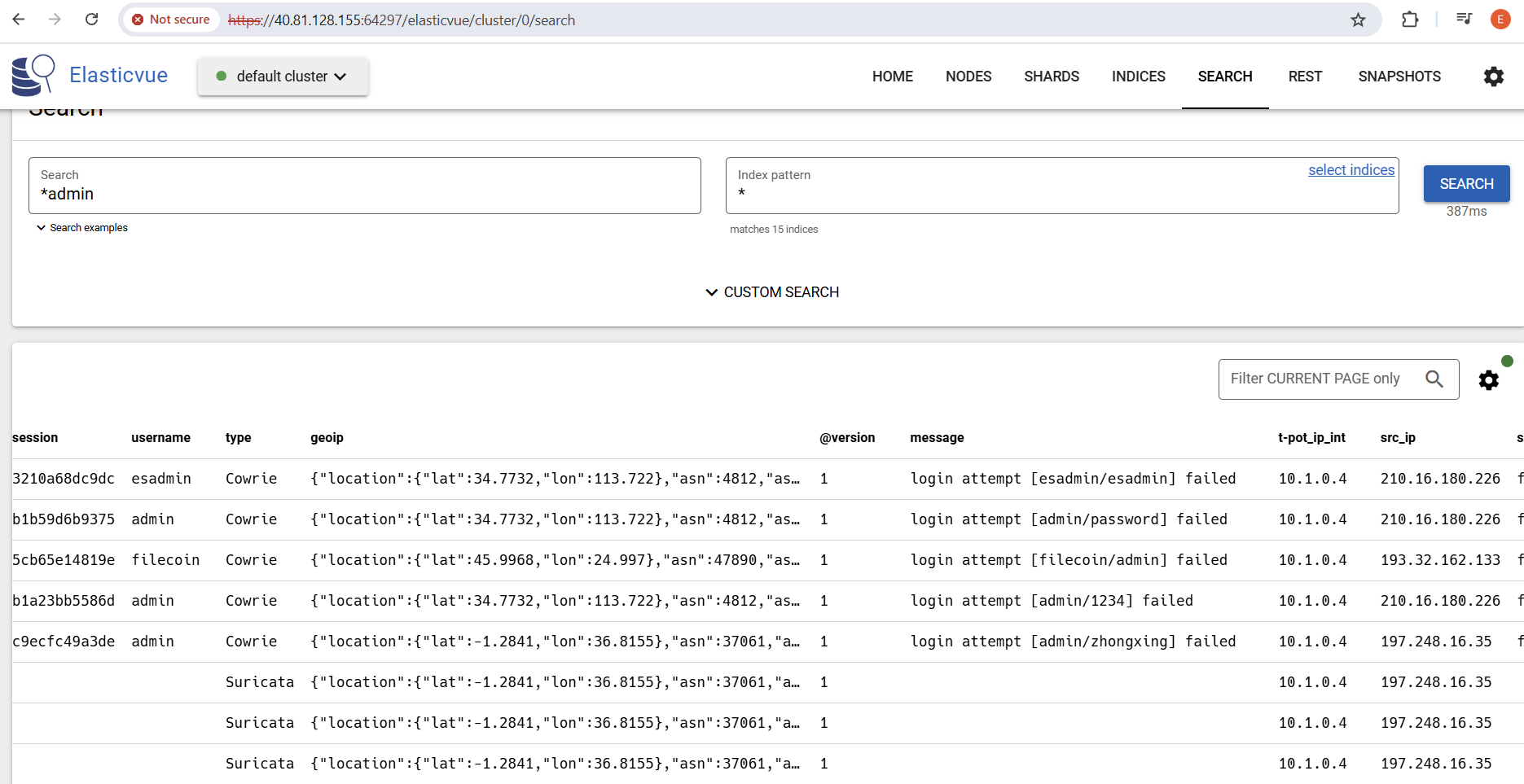
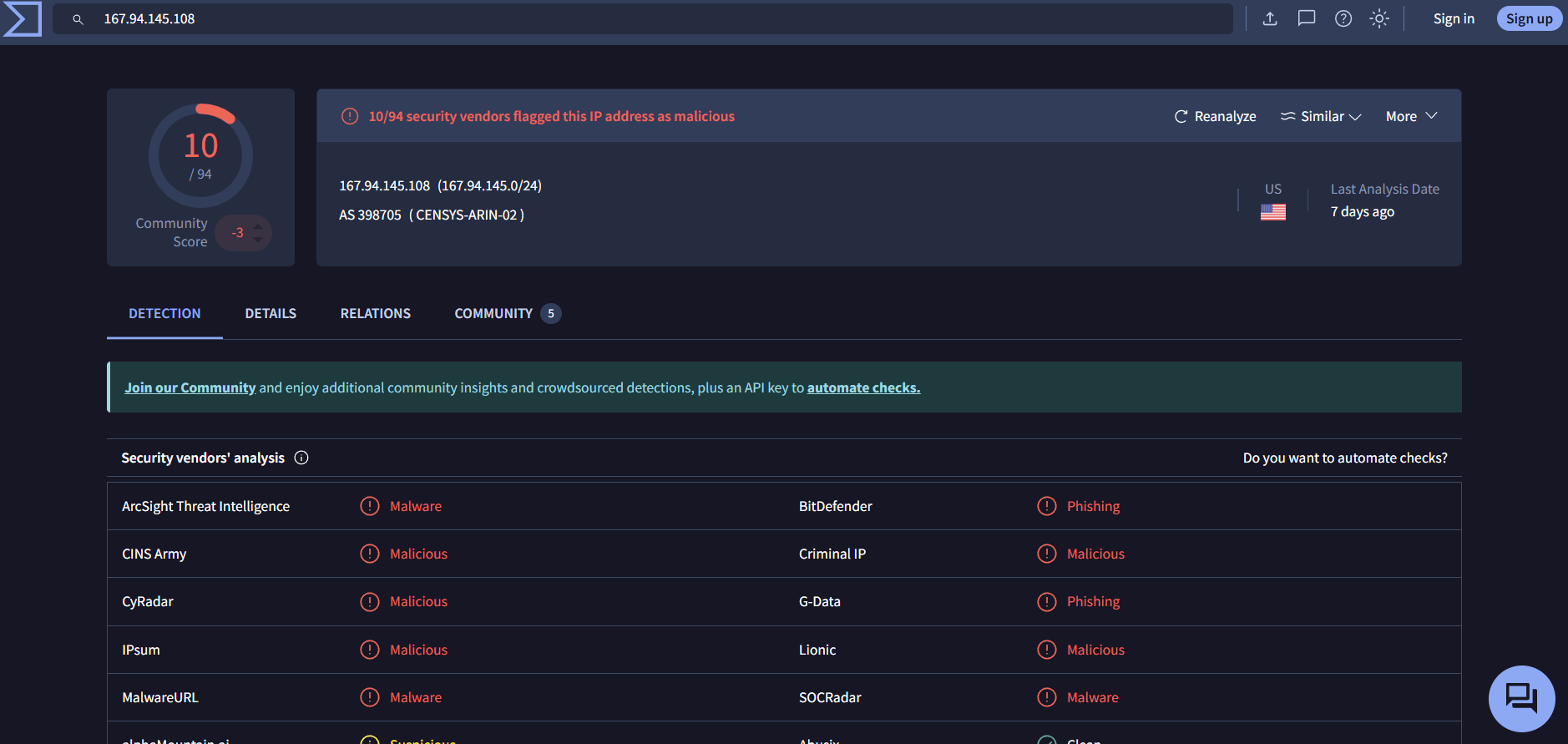
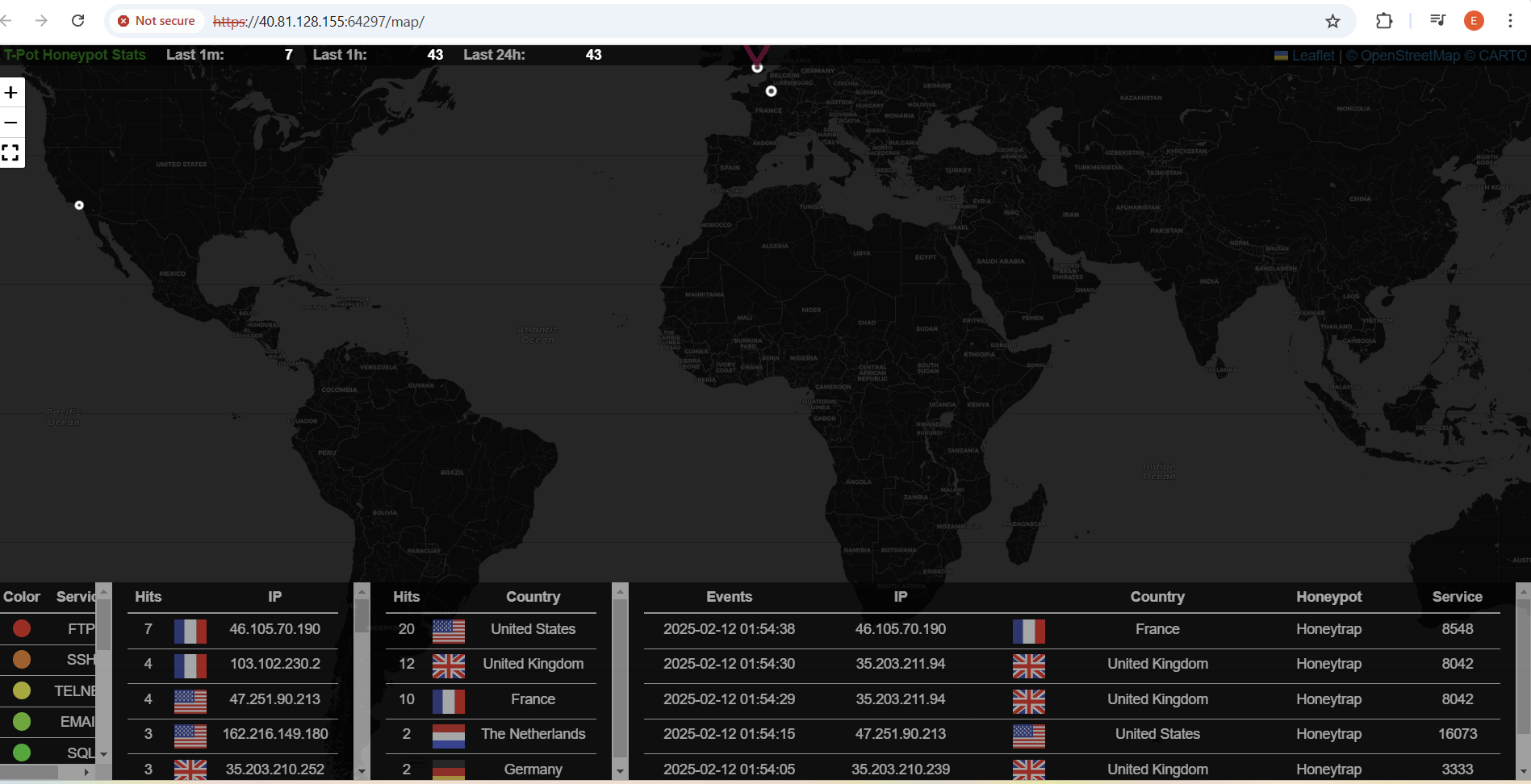
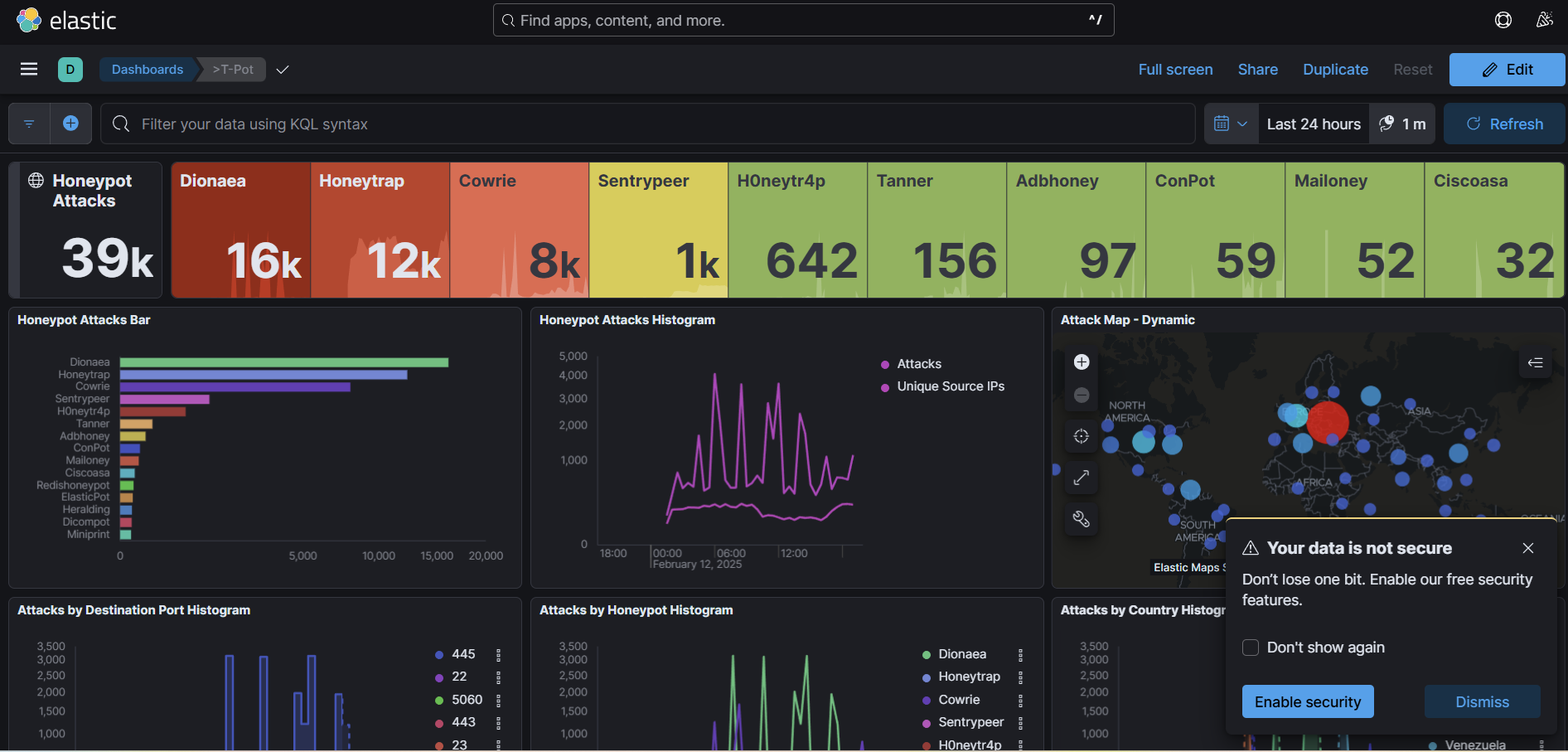
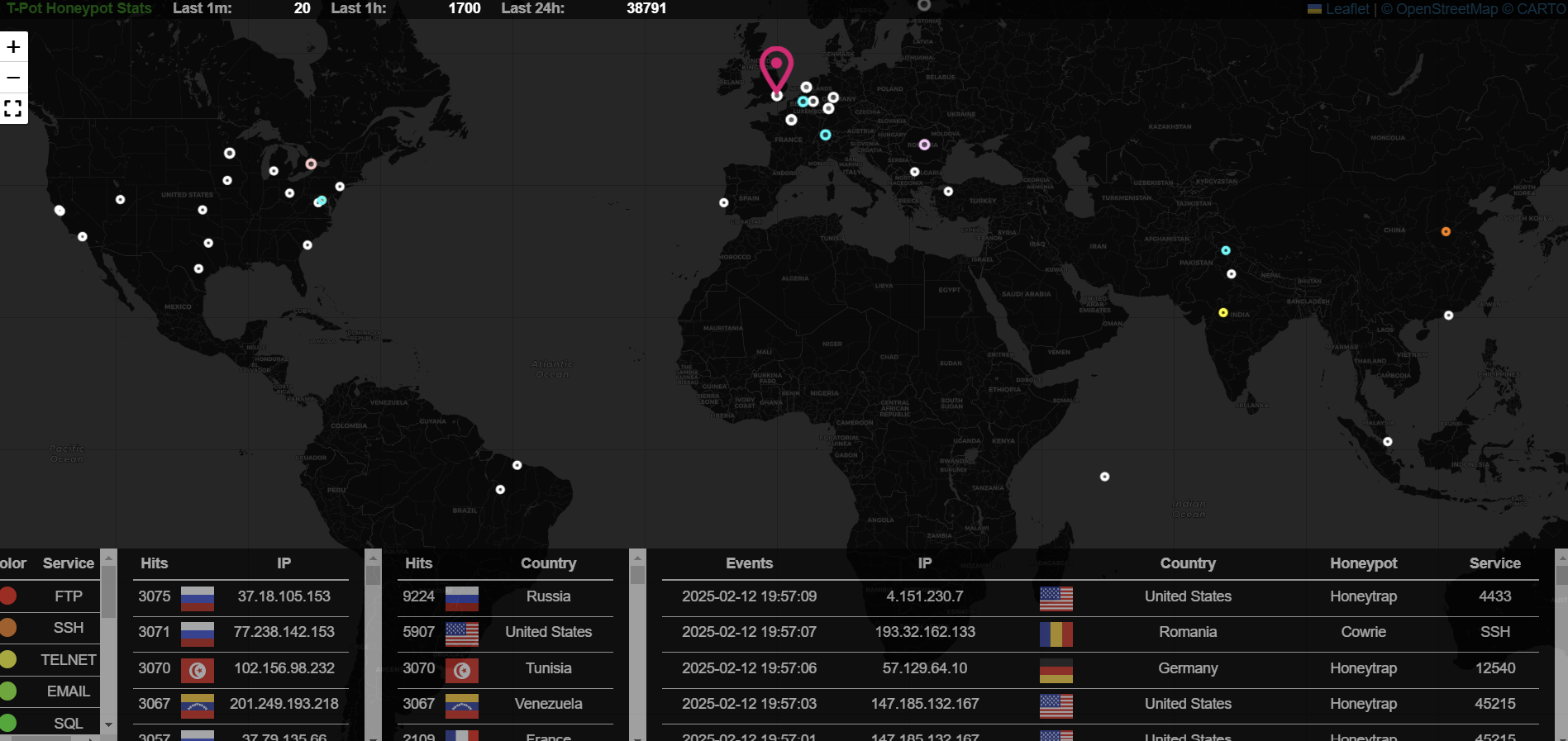
T-Pot, developed by Deutsche Telekom Security, is an all-in-one honeypot platform that integrates multiple honeypot technologies into a single deployment. The best part? It comes with a built-in web-based dashboard powered by Kibana, making log analysis and threat hunting much easier. Some key benefits include:
- Multiple honeypots (Cowrie, Dionaea, Snare, and more) running simultaneously.
- Pre-configured ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) for visualization.
- Dockerized setup for easy management.
- User-friendly web UI to monitor attacks in real-time.
Now, let's dive into setting it up on Azure
Prerequisite:
Before we get started, make sure you’ve got these basics covered:
An Azure Account: If you don’t have one, you can sign up for a free Azure account. They give you some free credits to play around with, which is perfect for this setup.
Basic Azure Knowledge: You don’t need to be an expert, but knowing how to create a virtual machine (VM) and configure networking will help.
An SSH Client: You’ll need this to connect to your VM. If you’re on Windows, PuTTY works great. On macOS or Linux, you can use the built-in terminal.
Step 1: Spin Up a Virtual Machine on Azure
Log in to Azure Portal - Head over to Azure Portal and sign in.
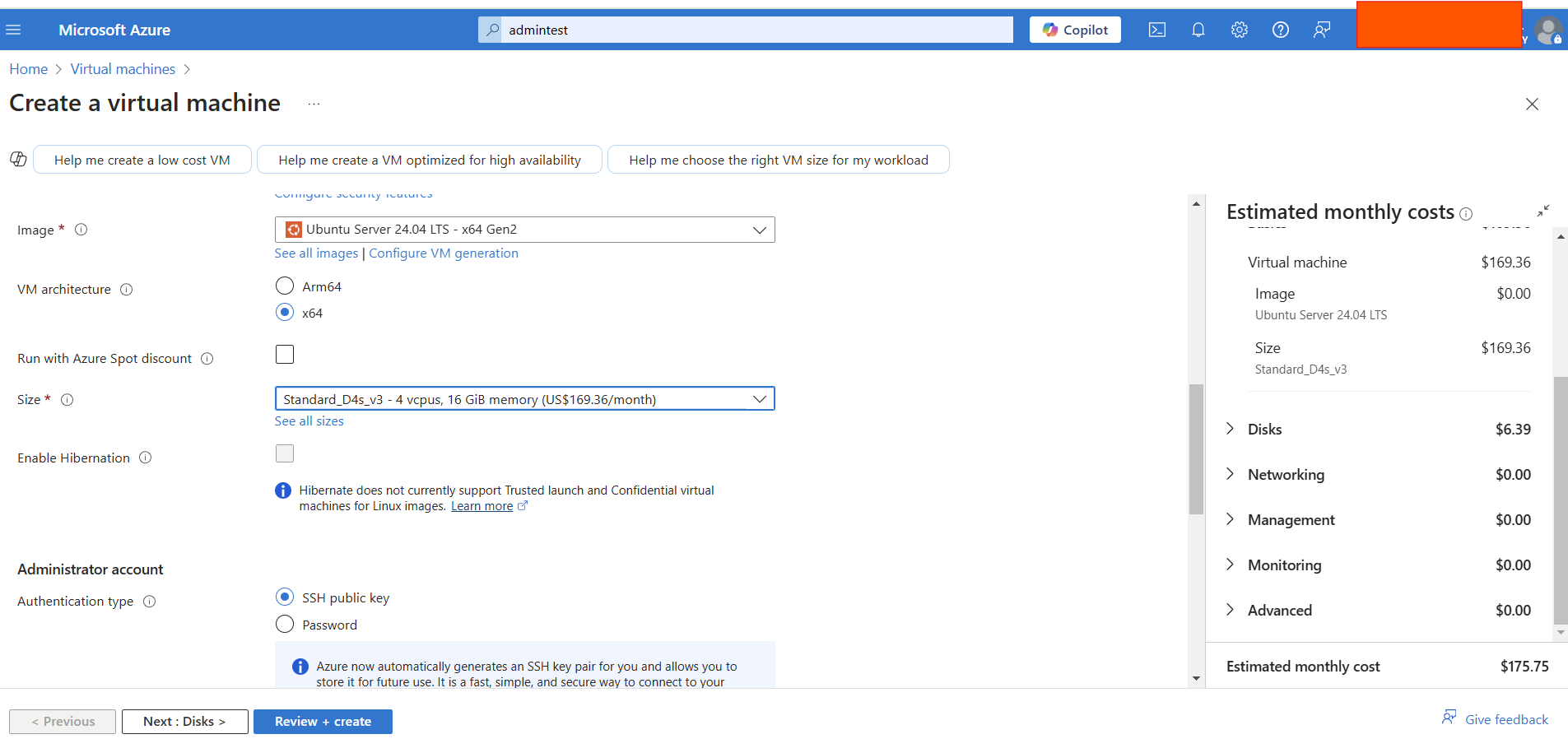
Create a new Virtual Machine:
- Click Create a resource > Compute > Ubuntu Server (Choose Ubuntu 20.04 LTS for compatibility).
- Select an appropriate VM size (T-Pot requires at least 4 vCPUs and 8GB RAM).
- Set up a username and SSH key for access.
Configure networking:
-Allow SSH (port 22), HTTP (port 80), and HTTPS (port 443).
-Add custom inbound rules for ports 64297, 64298, 64299 (T-Pot UI ports).
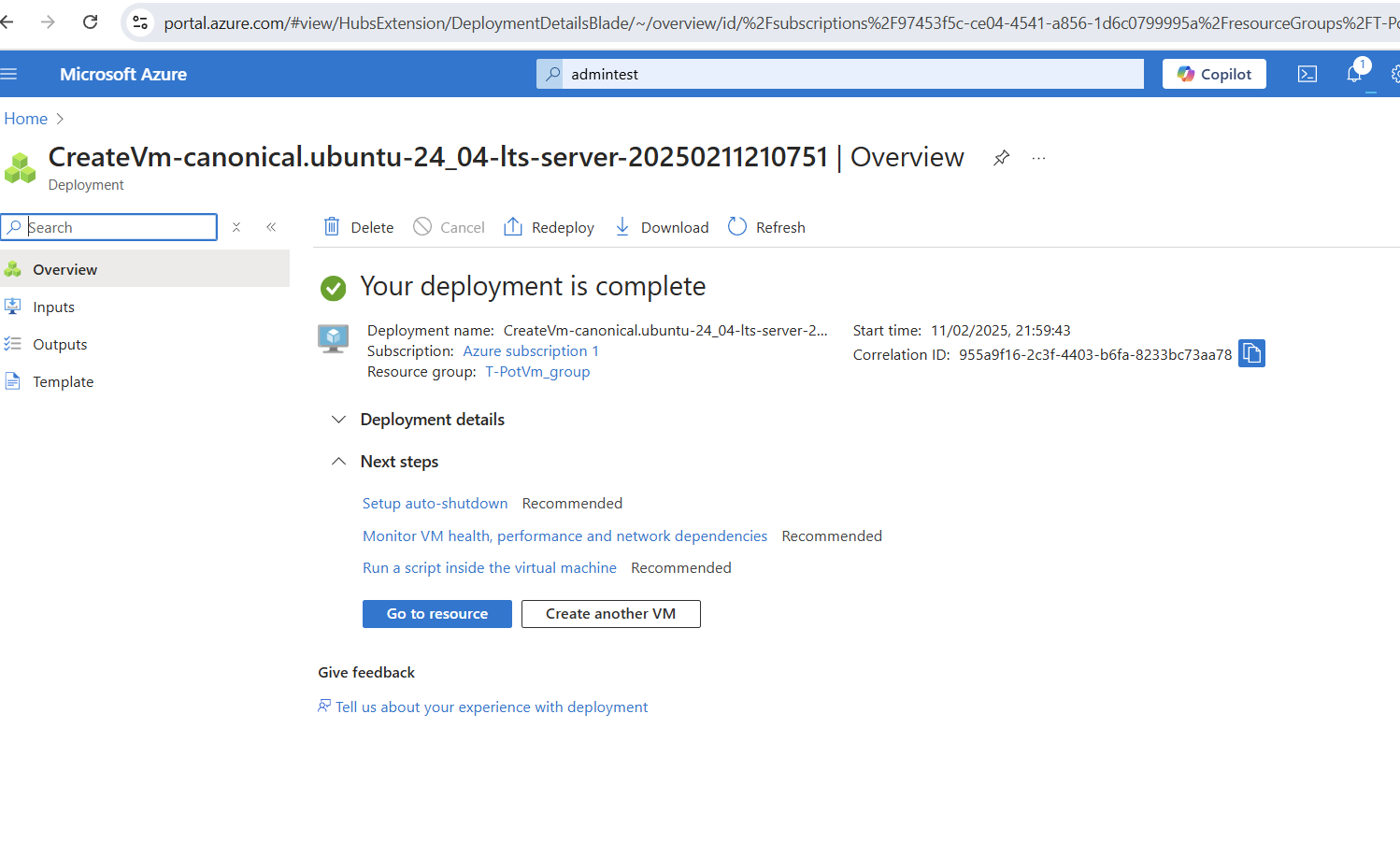
Review & Create - Click Create, and wait for Azure to provision your VM.